Meet Our Doctor

Dr. Prajaktam M. Lende
ORTHOPAEDIC & JOINT REPLACEMENT SURGEON
Fellowships
- Navigation Based Joint Replacement Surgery (Hip & Knee Arthroplasty)
- Arthroscopy & Sport Medicine
- Ilizarove Surgery
- Observer Ship in Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery (Wadia Hospital, Mumbai)
Best Knee Arthroscopy In Nagpur
Home / Best Knee Arthroscopy In Nagpur
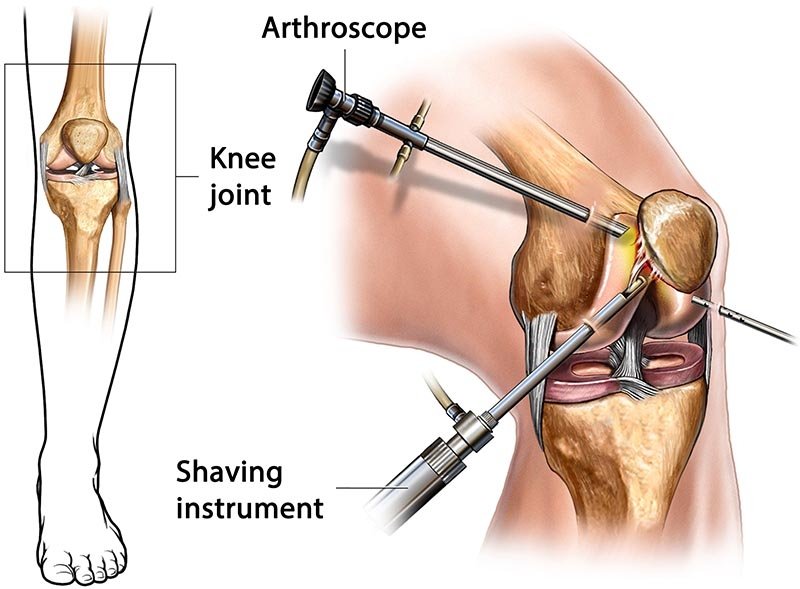
Best Knee Arthroscope
Knee arthroscopy a surgical treatment that permits doctors to look at the ginglymoid joint while not creating an oversized incision (cut) through the skin and alternative soft tissues. surgery is employed to diagnose and treat a large vary of knee issues.
throughout knee surgery, your doctor inserts alittle camera, referred to as AN endoscope, into your ginglymoid joint. The camera displays photos on a video monitor, and your doctor uses these pictures to guide miniature surgical instruments.
Because the endoscope and surgical instruments ar skinny, your doctor will use terribly tiny incisions, instead of the larger incision required for open surgery. This leads to less pain and joint stiffness for patients, and infrequently shortens the time it takes to recover and come back to favorite activities.
Anatomy of the Knee
Your knee is that the largest joint in your body and one in all the foremost complicated. The bones that conjure the knee embody the lower finish of the thighbone (thighbone), the higher finish of the shin (shinbone), and therefore the patella (kneecap).
Other necessary structures that conjure the ginglymoid joint include:
Articular animal tissue. The ends of the thighbone and shin, and therefore the back of the patella ar lined with body part animal tissue. This slippery substance helps your knee bones glide swimmingly across one another as you bend or straighten your leg.
Synovium. The ginglymoid joint is enclosed by a skinny lining referred to as tissue layer. This lining releases a fluid that lubricates the animal tissue and reduces friction throughout movement.
Meniscus. 2 wedge-shaped items of meniscal animal tissue between the thighbone and shin act as shock absorbers. totally different from body part animal tissue, the cartilage is hard and rubbery to assist cushion and stabilize the joint.
Ligaments. Bones ar connected to alternative bones by ligaments. The four main ligaments in your knee act like sturdy ropes to carry the bones along and keep your knee stable.
The two collateral ligaments ar found on either facet of your knee.
The two cruciform ligaments ar found within your ginglymoid joint. They cross {each other|one ANother} to create an X with the anterior cruciform ligament ahead and therefore the posterior cruciform ligament in back.
Preparing for Arthroscopy
Evaluations and Tests
Your medical science doctor could suggest that you simply see your primary doctor to assess your general health before your surgery. they’re going to establish any issues which will interfere with the procedure. If you have got bound health risks, a additional intensive analysis is also necessary before your surgery.
To help set up your procedure, your medical science doctor could order operative tests. These could embody blood tests or AN graph (EKG).
Admissions directions
If you’re typically healthy, your knee surgery can possibly be performed as AN patient procedure. this implies you’ll not got to keep nightlong at the hospital.
Be sure to tell your medical science doctor of any medications or supplements that you simply take. you will got to stop taking a number of these before surgery.
The hospital or surgery center can contact you before time to supply specific details concerning your procedure. ensure to follow the directions on once to arrive and particularly on once to prevent uptake or drinking before your procedure.
Anesthesia
Before your surgery, a member of the physiological state team can speak with you. Knee surgery are often performed beneath native, regional, or general anesthesia:
Local physiological state numbs simply your knee
Regional anesthesia numbs you below the waist
General physiological state puts you to sleep
Your medical science doctor and your specialist can discuss with you concerning that methodology is best for you.
Description
Three differing kinds of pain relief (anesthesia) is also used for knee surgery surgery:
Local anesthesia. Your knee is also numbed with pain drugs. you will even be given medicines that relax you. you’ll sit up.
Spinal physiological state. this can be conjointly referred to as regional anaesthesia. The pain drugs is injected into an area in your spine. you’ll be awake however won’t be able to feel something below your waist.
General anesthesia. you’ll be asleep and unpainful.
Regional nerve block (femoral or adductor muscle canal block). this can be another form of regional anaesthesia. The pain drugs is injected round the nerve in your groin. you’ll be asleep throughout the operation. this sort of physiological state can block out pain so you wish less general anaesthesia.
A cuff-like device is also place around your thigh to assist management haemorrhage throughout the procedure.
What are the advantages of knee arthroscopy?
Minimally invasive procedures like knee arthroscopy usually require less recovery time than traditional (open) surgery. As you only need a few small stitches, you’re more likely to get back on your feet more quickly than with traditional surgery. You may also have less pain and a lower risk of infection.
What are the risks or complications of knee arthroscopy?
Complications from knee arthroscopy are rare. As with any surgery, risks of knee arthroscopy include bleeding and infection.
After the procedure, some people have:
- Blood clots.
- Knee stiffness.
- Swelling that results from blood pooling in the knee (this complication is uncommon).
What conditions does knee arthroscopy treat?
You may need knee arthroscopy if you have:
Fracture: Bones can break or chip off inside of your knee. Sometimes, pieces of cartilage (rubbery tissue that helps bones move against each other smoothly) can break off when your bone fractures.
Inflammation: The synovium inside a joint can become inflamed (swollen and irritated). Synovium is soft tissue on the inside of a joint. Healthcare providers call this condition synovitis.
Best AVN treatment In Nagpur
Dr. Prajaktam Lende is a trusted Orthopedic doctor In Nagpur. Top joint Replacement surgery Doctor in Nagpur. Book an Appointment with Dr Prajaktam M. Lende, one of the prominent orthopaedic surgeon specialised in Joint Replacement surgery and ligament Reconstruction surgery Dr Prajaktam M. Lende at Nagpur. He is currently associated with the Orthopedic & Joint …
