Meet Our Doctor

Dr. Prajaktam M. Lende
ORTHOPAEDIC & JOINT REPLACEMENT SURGEON
Fellowships
- Navigation Based Joint Replacement Surgery (Hip & Knee Arthroplasty)
- Arthroscopy & Sport Medicine
- Ilizarove Surgery
- Observer Ship in Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery (Wadia Hospital, Mumbai)
Hip replacement In Harda
Home / Hip replacement In Harda
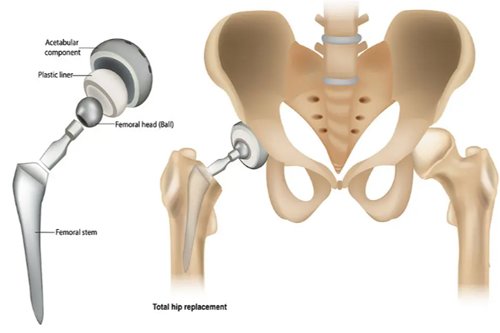
Hip replacement In Harda, also known as total hip arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which a damage or disease hip joint is replace with an artificial joint, call a prosthesis.
The hip joint consists of a ball (femoral head) at the top of the thigh bone (femur), which fits into a socket (acetabulum) in the pelvic bone. Conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, avascular necrosis, or severe hip fractures can lead to significant pain and limit mobility, often necessitating a total hip replacement.
The surgical process involves removing the damage femoral head and replacing it with a metal or ceramic ball mount on a stem, which is insert into the femur.
Treatment and Recovery Process for Total Hip Replacement
Total hip replacement, also known as hip arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure commonly perform to relieve pain and restore function in individuals with severe hip joint damage, often cause by osteoarthritis or other degenerative conditions. The procedure involves replacing the damage hip joint with an artificial joint, typically made of metal and plastic components. Here is an overview of the treatment and recovery process for total hip replacement:
Surgical Procedure:
- Anesthesia:
- Total hip replacement is usually perform under general anesthesia, although regional anesthesia options may be consider.
- Incision:
- An incision is made to access the hip joint. The size and location of the incision may vary.
- Hip Joint Resurfacing:
- Damage cartilage and bone are remove from the hip socket and femoral head.
- Implant Placement:
- The artificial hip components (acetabular cup, femoral stem, and sometimes a femoral head) are securely implant.
- Closure:
- The incision is close, and the surgical site is dress.
Postoperative Care:
- Hospital Stay:
- Most patients stay in the hospital for a few days, but this can vary.
- Thus,Physical therapy begins shortly after surgery to aid in mobility and prevent complications.
- Pain Management:
- Therefore, Medications are prescribe to manage postoperative pain.
- Prevention of Blood Clots:
- Blood thinners and compression stockings may be use to reduce the risk of blood clots.
- Early Ambulation:
- Patients are encourage to begin walking with the help of crutches or a walker soon after surgery.
Rehabilitation and Recovery:
- Physical Therapy:
- Firstly,A structure physical therapy program helps improve joint flexibility, strength, and overall function.
- Once,Rehabilitation may continue on an outpatient basis.
- Activity Modification:
- Thus,Patients are advise on movement restrictions and gradual return to daily activities.
Long-Term Considerations:
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Firstly,Patients may need to make adjustments to their lifestyle and activities to protect the artificial joint.
- Routine Check-ups:
- once, Periodic follow-up visits with the orthopedic surgeon to assess the condition of the hip replacement.
- Complications Monitoring:
- Thus, While complications are rare, it’s important to monitor for signs of infection, implant loosening, or other issues.
During the procedure
The surgical procedure can be completed within two hours. To perform a hip replacement, the surgeon:
- Makes an incision over the hip, through the layers of tissue.
- Removes diseased and damaged bone and cartilage, preserving the healthy bone.
- Implants the replacement socket into the pelvic bone.
- Inserts a metal stem into the top of the thighbone, which is then topped with a replacement ball.
Common Causes of Hip Pain
The most common cause of chronic hip pain and disability is arthritis, which includes osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and posttraumatic arthritis.
Osteoarthritis: This age-related wear-and-tear type of arthritis usually occurs in people aged 50 and older, often in those with a family history of arthritis. The cartilage cushioning the hip bones wears away, causing the bones to rub against each other, leading to hip pain and stiffness. Osteoarthritis can also be caused or accelerated by subtle irregularities in hip development during childhood.
Rheumatoid arthritis: This autoimmune disease causes the synovial membrane to become inflamed and thickened. Chronic inflammation can damage the cartilage, resulting in pain and stiffness. Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common type of inflammatory arthritis.
Posttraumatic arthritis: This type of arthritis can develop after a serious hip injury or fracture. Damaged cartilage may lead to hip pain and stiffness over time.
Osteonecrosis: An injury to the hip, such as a dislocation or fracture, may restrict blood supply to the femoral head, leading to osteonecrosis (also known as avascular necrosis). The lack of blood can cause the bone surface to collapse, resulting in arthritis. Some diseases can also cause osteonecrosis.
Childhood hip disease: Some infants and children have hip problems that, even when successfully treated during childhood, may cause arthritis later in life. This occurs because the hip may not grow normally, affecting the joint surfaces. For more information, see Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) and Adolescent Hip Dysplasia.
Best AVN treatment In Harda
Dr. Prajaktam Lende is a trusted Orthopedic doctor In Harda. Top joint Replacement surgery Doctor in Harda. Book an Appointment with Dr Prajaktam M. Lende, one of the prominent orthopaedic surgeon specialised in Joint Replacement surgery and ligament Reconstruction surgery Dr Prajaktam M. Lende at Harda. He is currently associated with the Orthopedic & Joint …
